Weight loss surgery, often referred to as Bariatric surgery, serves as a pivotal turning point for individuals grappling with obesity and related health issues.
Other common names for Weight Loss surgery are
- Gastric Bypass Surgery
- Obesity Surgery
- Fat Removal Surgery
- Gastric Surgery
- Metabolic Surgery
These surgical interventions aim to modify the digestive system to help patients achieve significant weight loss.
Not just a quick fix, these surgeries also necessitate long-term lifestyle changes for sustainable results.
Ideal for those who have exhausted other weight loss methods without success, weight loss surgery could be a life-saving option worth considering.
Read on to explore the various types, benefits, and risks associated with this transformative medical approach.
Which Doctor Performs Weight Loss Surgery?
Weight loss surgeries are typically performed by surgeons who specialize in bariatric procedures. These medical professionals are often referred to as bariatric surgeons.
Bariatric surgeons have completed specialized training in the surgical treatment of obesity and related conditions, in addition to their general surgical training.
It’s essential to seek a qualified and experienced bariatric surgeon who is affiliated with an accredited medical council in their state and country. This ensures that both the surgeon and the healthcare institution meet rigorous standards for patient care and safety.
Many bariatric surgeons are also members of professional organizations like the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) or similar bodies in other countries, which further validates their expertise in this medical specialty.
Before undergoing weight loss surgery, patients usually go through a comprehensive evaluation process, including consultations with nutritionists, psychologists, and other medical specialists to determine if they are suitable candidates for the procedure.
Different Types of Weight Loss Surgery in India
A. Gastric Bypass
B. Sleeve Gastrectomy
C. Adjustable Gastric Banding
D. Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch
A. Gastric Bypass
1. Definition and Description
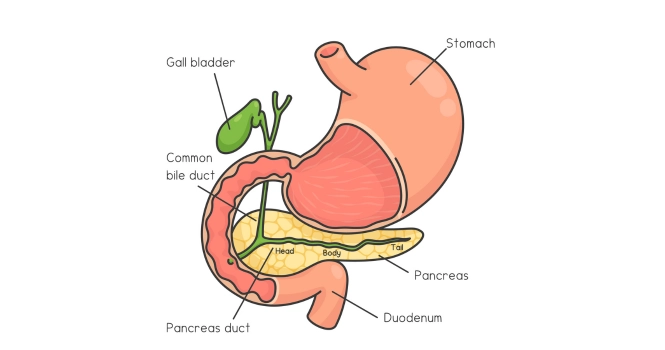
Gastric bypass, formally known as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB), is one of the most common types of bariatric surgery. It involves creating a small stomach pouch and bypassing a portion of the small intestine.
This process not only limits the amount of food intake but also reduces the body’s ability to absorb nutrients from food. This dual mechanism results in significant weight loss.
2. Procedure
The surgery is performed under general anesthesia. The surgeon begins by making a small pouch out of the top portion of the stomach, usually through a laparoscopic approach.
The new stomach pouch is then directly connected to the middle section of the small intestine (the jejunum), bypassing the rest of the stomach and the upper section of the small intestine (the duodenum). This reduces the calories and nutrients the body can absorb.
3. Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- High Success Rate: Gastric bypass surgery has a high success rate and has been shown to result in significant weight loss.
- Health Improvement: It can also lead to improvement or resolution of obesity-related conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and sleep apnea.
- Satiety: The smaller stomach pouch can increase feelings of fullness, helping to reduce calorie intake.
Disadvantages:
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Since the surgery affects nutrient absorption, patients may need to take supplements for the rest of their lives to prevent nutritional deficiencies.
- Surgical Risks: As with any major surgery, there are risks, such as infections, bleeding, and reactions to anesthesia. There is also a risk of dumping syndrome, which can cause nausea, vomiting, and other issues.
- Non-Reversible: Gastric bypass is difficult to reverse if complications occur.
- Requires Significant Lifestyle Changes: To maintain weight loss, patients must adhere to a healthy diet and regular exercise.
B. Sleeve Gastrectomy
1. Definition and Description
A sleeve gastrectomy, often referred to simply as the ‘sleeve’, is a surgical weight-loss procedure that involves removing approximately 80% of the stomach.
The remaining portion of the stomach is formed into a tubular structure resembling a banana. This surgery not only restricts the amount of food intake due to the smaller stomach size but may also affect hunger hormones, thus suppressing appetite.
2. Procedure
The surgery is performed under general anesthesia, and typically via a laparoscopic approach. The surgeon starts by making small incisions in the abdomen.
A laparoscope along with other surgical instruments are inserted through these incisions. The majority of the stomach is then removed, and the remaining portion is formed into a tube-like structure. This new stomach is significantly smaller, thus limiting the amount of food it can hold.
3. Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- Weight Loss: Most people lose 60% to 70% of their excess weight within two years of surgery.
- Improvement in Health Conditions: Conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and sleep apnea can significantly improve following surgery.
- No Foreign Objects and Less Complex: Unlike other procedures like the gastric band, there are no adjustments needed and no foreign objects left in the body.
Disadvantages:
- Irreversible: The procedure is irreversible as a large part of the stomach is removed.
- Vitamin Deficiencies: As with other forms of bariatric surgery, vitamin and mineral deficiencies can occur, requiring lifelong supplementation.
- Surgical Complications: Potential complications include leaks from the staple line, blood clots, and infections. Sleeve gastrectomy may also cause gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or worsen the condition in people who already have it.
- Requires Lifestyle Changes: Patients need to make significant long-term lifestyle changes, including diet and exercise, to ensure the success of the surgery.
C. Adjustable Gastric Banding
1. Definition and Description
Adjustable gastric banding, often known by the brand name Lap-Band, is a type of weight loss surgery that involves placing a band around the upper part of the stomach to create a small pouch.
This pouch can hold only a small amount of food, helping to limit food intake and promote a feeling of fullness.
2. Procedure
The procedure is performed under general anesthesia using a laparoscopic approach. The surgeon places a silicone band around the top part of the stomach, creating a small pouch above the band with a narrow opening to the rest of the stomach.
The band is adjustable and can be tightened or loosened to control the size of the passage by injecting or removing saline solution through a port placed under the skin.
3. Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- Adjustability: The band can be adjusted based on the patient’s weight loss progress and appetite.
- Reversible: Unlike some other forms of bariatric surgery, the procedure is reversible. The band can be removed if necessary.
- Lower Risk: It has a lower risk of surgical complications compared to more invasive procedures like gastric bypass.
Disadvantages:
- Slower Weight Loss: Weight loss is generally slower and less dramatic compared to other forms of weight loss surgery.
- Possible Band Complications: The band may slip or erode into the stomach, or the port may become infected. The band may also not provide enough weight loss or may result in complications, necessitating additional surgery.
- Regular Follow-ups: Regular adjustments to the band tightness require frequent follow-up visits to the doctor.
- Lifestyle Changes: As with all bariatric surgeries, the patient will need to commit to significant dietary and lifestyle changes to achieve and maintain weight loss.
D. Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch
1. Definition and Description
Biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD/DS) is a more complex type of bariatric surgery that combines restrictive and malabsorptive aspects.
It involves both reducing the size of the stomach and rerouting the small intestine to limit calorie absorption. It is generally recommended for individuals with a higher body mass index (BMI) or Uncontrolled diabetes.
2. Procedure
The procedure is done in two parts and usually under general anesthesia. The first part is similar to a sleeve gastrectomy where about 70% of the stomach is removed.
The second part, the duodenal switch, involves rerouting a significant part of the small intestine to create two separate pathways and one common channel. The shorter pathway carries food from the stomach to the common channel and the longer pathway carries bile from the liver to the common channel.
The place where the pathways meet is where digestion happens. This design significantly reduces the body’s ability to absorb calories and nutrients.
3. Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- Greater Weight Loss: BPD/DS often results in greater weight loss than other bariatric surgeries. Most people lose 70-80% of their excess weight within two years.
- Long-Term Weight Loss: It has the highest rate of maintained weight loss long term.
- Improves Health Conditions: It can significantly improve obesity-related health conditions, including diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol, and sleep apnea.
Disadvantages:
- Complex Procedure: BPD/DS is a more complex operation and has higher complication and mortality rates.
- Nutrient Deficiencies: The procedure can lead to deficiencies in vitamins, minerals, and protein because it significantly impairs the ability to absorb nutrients. Lifelong supplements are required.
- More Follow-Up Care: Patients need more regular follow-ups due to the high risk of health problems.
- Requires Serious Lifestyle Changes: Patients must adhere to a strict, lifelong diet and vitamin regimen.
Criteria for Weight Loss Surgery
A. Body Mass Index (BMI) Requirements
In general, weight loss surgery may be an option for adults with a Body Mass Index (BMI) of 40 or higher. For individuals with serious health problems related to obesity, such as type 2 diabetes or sleep apnea, surgery may be considered with a BMI of 35 to 39.9.
B. Previous Attempts at Weight Loss
Typically, weight loss surgery is considered only after traditional methods of weight loss, including diet and exercise, have been tried without success. Patients are usually required to provide documented evidence of their failed attempts to lose weight through non-surgical methods.
C. Evaluation of Potential Psychological Impact
Psychological evaluation is an essential part of the pre-surgery assessment. It helps to determine if a patient is mentally prepared for the surgery and the lifestyle changes that come with it.
Issues such as untreated eating disorders, depression, or substance abuse may interfere with the success of the surgery.
D. Risk Assessment
A comprehensive medical evaluation is conducted to assess the patient’s overall health and the potential risks of the surgery. This includes evaluation of heart health, lung function, kidney function, and liver function.
The patient’s age and the presence of any obesity-related conditions like diabetes, heart disease, or high blood pressure will also be considered. The benefits of the surgery need to significantly outweigh the risks for a patient to be considered a suitable candidate.
Pre-Surgery Preparations
A. Medical Evaluation and Tests
Prior to surgery, patients undergo a thorough medical evaluation to assess their overall health and fitness for the procedure. This may include blood tests, imaging studies, a sleep apnea screening, heart and lung evaluations, and any other tests deemed necessary by the surgical team. Patients may also need to lose some weight before surgery to reduce surgical risk.
B. Nutritional Counseling
A registered dietitian is often involved in pre-surgery preparation to educate patients about the dietary changes required both before and after surgery.
This includes understanding portion control, balanced meals, and nutritional needs post-surgery. They may also discuss the importance of hydration, vitamin and mineral supplements, and recognizing signs of nutrient deficiencies.
C. Psychological Evaluation
Patients undergo a psychological evaluation to determine their readiness for surgery and the lifestyle changes required afterward.
This evaluation helps identify any mental health conditions, substance abuse issues, or behavioral factors that could affect the patient’s ability to adhere to post-surgery guidelines.
D. Lifestyle Changes
Preparing for bariatric surgery involves making significant lifestyle changes. Patients are often required to begin these changes prior to surgery, including adopting a healthier diet, starting a physical activity regimen, quitting smoking, and reducing or eliminating alcohol consumption.
The goal is to establish healthier habits that will aid in recovery and long-term success after surgery.
Post-Surgery Care and Recovery
A. Hospital Stay and Immediate Post-Surgery Care
The length of the hospital stay varies depending on the type of weight loss surgery performed and the patient’s overall health.
During the stay, the healthcare team will manage pain, monitor vital signs, and watch for any signs of complications. The patient will typically start on a liquid diet and gradually transition to soft foods before returning to solid foods.
B. Diet and Nutrition
After surgery, patients must adhere to a strict diet plan to allow the stomach to heal and to adapt to its new structure.
This typically starts with a liquid diet, followed by pureed food, then soft foods, and eventually a diet of nutrient-dense, portion-controlled solid foods. To prevent nutrient deficiencies, patients will also need to take vitamin and mineral supplements for the rest of their lives.
C. Exercise and Physical Therapy
Exercise is an essential component of the post-surgery lifestyle. Initially, patients are encouraged to engage in light activities such as walking.
As they recover, they will gradually transition to more intensive exercises. A physical therapist may guide the patient through appropriate exercises to aid in recovery and promote weight loss.
D. Long-Term Follow-up and Support
Regular follow-up visits are crucial after weight loss surgery to monitor the patient’s health, weight loss progress, nutritional status, and mental health.
These visits may include consultations with the surgeon, dietitian, psychologist, and a support group. The aim is to ensure the patient is adjusting well physically and emotionally to the changes and is following the necessary lifestyle modifications.
Risks and Complications of Weight Loss Surgery
A. Short-term Risks and Complications
- Surgical Complications: As with any surgery, there are inherent risks, including infection, excessive bleeding, blood clots, and adverse reactions to anesthesia.
- Postoperative Complications: Early complications may include leaks from the site where the intestine is sewn to the stomach in procedures like gastric bypass, wound infections, or pulmonary embolisms.
B. Long-term Risks and Complications
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Because the surgeries affect digestion, there’s a risk of nutritional deficiencies. Patients may need to take dietary supplements for life.
- Dumping Syndrome: This can occur when food moves too quickly from the stomach to the small intestine, causing nausea, vomiting, bloating, diarrhea, and dizziness.
- Gallstones: Rapid weight loss can lead to the development of gallstones.
- Weight Regain: Some patients may regain some of the weight they lost as they adapt to the new dietary restrictions and stomach capacity.
C. Emotional and Psychological Considerations
- Changes in Body Image: Drastic changes in weight and body shape can lead to issues with body image and self-esteem.
- Emotional Changes: Some individuals may experience mood swings, depression, or anxiety after surgery.
- Relationship Changes: Changes in lifestyle, activities, and appearance can affect relationships with family, friends, and partners.
- Substance Abuse: Some patients may develop substance abuse problems after surgery, potentially as a result of swapping one addiction (food) for another (drugs or alcohol).
Effectiveness of Weight Loss Surgery
A. Weight Loss Expectations
Weight loss surgery can lead to significant weight loss. The amount varies based on the type of surgery and the patient’s commitment to lifestyle changes.
On average, patients may lose 30% to 40% of their total body weight within the first six months, and may reach a maximum of 60% to 85% within two years, depending on the procedure.
B. Impact on Obesity-Related Health Conditions
Bariatric surgery can greatly improve, and in some cases completely resolve, obesity-related health conditions such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease, sleep apnea, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and certain types of cancer.
C. Quality of Life Improvements
Beyond the physical benefits, weight loss surgery often leads to significant improvements in quality of life.
This can include enhanced mobility, better mood and self-esteem, improved social and economic opportunities, and an overall increase in life satisfaction.
However, it’s important to remember that the journey involves substantial physical and emotional adjustments and commitment to lifelong dietary, exercise, and medical guidelines.
Alternatives to Surgery
A. Diet and Exercise
A balanced diet and regular physical activity remain the cornerstone of weight management.
In many cases, with the guidance of a dietitian or a weight loss counselor, individuals can achieve and maintain a healthy weight by following a comprehensive weight loss program that includes a low-calorie diet, a regular exercise regimen, and behavior changes.
B. Medications
There are several weight loss medications that can be used as an alternative or addition to lifestyle changes.
These medications, which must be prescribed by a healthcare provider, work in various ways, such as reducing appetite, increasing feelings of fullness, or reducing the body’s absorption of fat.
C. Non-surgical Procedures
In recent years, several non-surgical procedures have been developed to aid in weight loss.
These include intragastric balloons (a balloon is inserted into the stomach to reduce space), endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (the size of the stomach is reduced using an endoscope), and vagal nerve blockade (a device is implanted under the skin of the abdomen that sends electrical pulses to the vagus nerve to signal feelings of fullness).
These procedures are generally less effective than bariatric surgery but may be suitable for certain individuals.
Allurion Procedure
The Allurion procedure, often known as the “Allurion Balloon” or “Elipse Balloon,” is a non-surgical weight loss treatment designed to aid in significant weight reduction.
Unlike traditional bariatric surgeries like gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy, this procedure does not require anesthesia, incisions, or endoscopy.
The Elipse Balloon is a soft, expandable device that is swallowed in pill form. Once it reaches the stomach, it is inflated with a sterile fluid through a thin catheter, which is then removed.
The inflated balloon occupies space in the stomach, creating a sensation of fullness and thereby reducing the amount of food one can consume.
One of the unique features of the Allurion procedure is that the balloon is designed to self-deflate and pass naturally through the digestive system after approximately 16 weeks. This eliminates the need for a removal procedure.
Patients are generally able to resume their normal activities immediately after the balloon is inflated, making it a convenient option for those who are looking for a less invasive weight loss solution.
It’s important to note that the balloon is accompanied by a customized nutrition and lifestyle coaching program to help sustain long-term weight loss.
While the Allurion procedure has been celebrated for its convenience and non-surgical nature, it’s not suitable for everyone.
The treatment is typically recommended for individuals with a Body Mass Index (BMI) between 27 and 40, and who have had limited success with traditional weight loss methods.
It’s not a one-size-fits-all solution and won’t replace the need for a healthy diet and regular exercise. Potential side effects may include nausea, vomiting, and abdominal discomfort, especially during the first few days after the balloon is inflated.
As with any medical procedure, it’s crucial to consult with healthcare professionals for a comprehensive evaluation to determine if the Allurion procedure is the right choice for you.
Note : If you require any assistance or guidance regarding Weight Loss Surgery in India, then you could reach out to our Team, who would guide you in your journey.