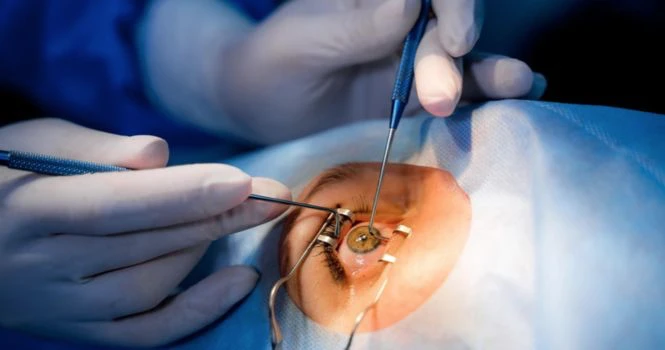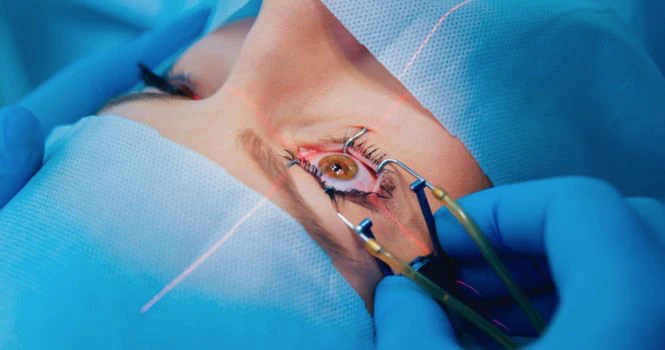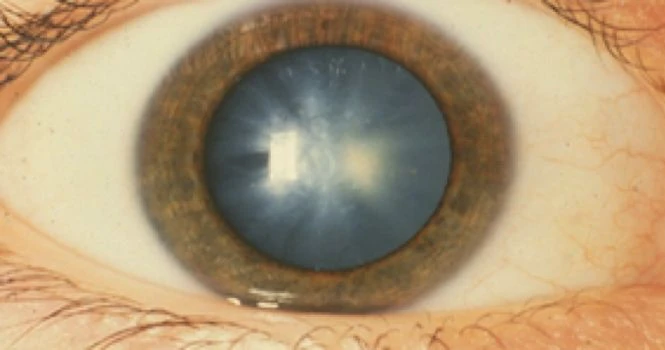
What is a Cataract?
The main purpose of your lens is to bend light rays that fall into your eyes and help you see. The lens should thus be clear. But when you have a cataract, it will be like viewing through a foggy or a dusty sheet. Your vision might get blurry, hazy or less colorful. To remove a cataract, your eye doctor will recommend a cataract surgery during which, your cloudy natural eye lens would be removed and replaced with a clear artificial lens.
What are the symptoms of Cataracts?
Cataract – a cloudy or opaque area in the normally clear lens of your eyes, mostly develops over the age of 55. But in rare cases, it does affect young children and even infants. Cataracts mostly develop in both the eyes, but one eye might be affected worse than the other.
Symptoms include:
- Blurry vision
- Glare
- Colors appearing faded
- Difficulty in reading
- Poor Night vision
- Double vision
- Frequent changes in eyeglass/contact lens prescriptions
Cataracts progress very slowly and you might not really need surgery for many years. Sometimes, just changing eyeglass or contact lens prescription can continue to help you with good vision.
Although prevention is key in most health conditions, there isn’t any way to prevent cataracts from developing in your eyes. At present, the only way to manage cataract is to surgically remove the affected lens and replacing it with a clear one.
What causes a Cataract?
Your eye lens is made of mostly water and protein. The protein is precisely arranged in such a way that it maintains the lens with clarity, allowing it to let light pass through it. With age, some of that protein might clump together and begin to cloud a small area of your lens and lead to cataract formation. And over time, the cataract might grow in size and cloud more of your lens and cause blurred vision. Other factors that can cause cataracts include smoking and diabetes.
How are cataracts detected?
Cataracts are discovered via comprehensive eye exams including:
- Dilated eye exams- where eye drops are placed to widen your eyes and your ophthalmologist uses a special magnifying lens to look into your retina and optic nerve to find any signs of damages.
- Tonometry- where they use an instrument to measure the pressure inside your eyes.
- Visual acuity tests that are performed using eye charts which help measure your vision at various distances.
How are cataracts treated?
When detected early, you can improve your symptoms via new eyeglasses, anti-glare sunglasses, magnifying lenses, etc. When all of these fail to help you, surgery can be the only treatment. You need cataract surgery only when you experience loss of vision that interferes with your daily activities like driving, reading and watching television. In rare cases, even when it doesn’t interfere with those everyday activities, but interferes with the treatment or examination of other eye problems, surgery is recommended. It is recommended that you take proper advice from your eye specialist.
How effective is cataract surgery?
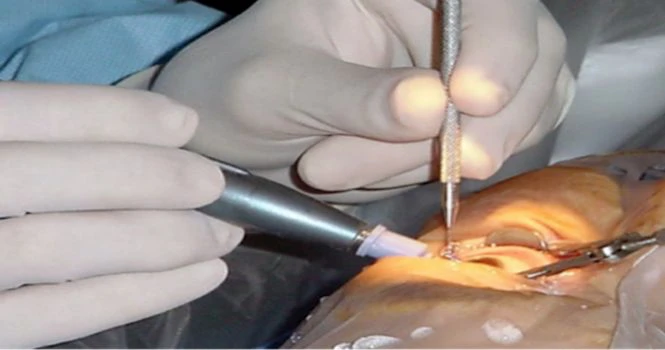
It is one of the most common, safest and effective surgeries. About 90% of individuals who underwent the surgery have reported better vision afterward.
What to expect after cataract surgery?
You can expect your vision to improve after a few days. Though it might be slightly blurred initially, once your eyes heal completely, it will get better. Also, colors will start appearing brighter since you will be looking through a new clear lens. You might also feel slightly itchy and experience slight discomfort for a few days. You will be asked to wear an eye patch or protective shield during sleep. Eye drops and other medications will be prescribed to prevent infection and reducing inflammation.
How risky is cataract surgery?
Similar to any other surgery, cataract surgeries also poses risks of infection and bleeding. It might slightly increase your risk of retinal detachment. If you notice any increase in eye floaters or flashes, it is recommended that you visit your eye specialist at the earliest and get treated immediately.
Here’s a list of possible problems/complications:
- Bleeding in the eye
- Eye infection
- Swelling of the front or inside of the eye
- Retinal swelling
- Detached retina
- Pain that doesn’t reduce with Prescription medicine
- Loss of vision
- Dislocation of the IOL implant
Can cataract recur after surgery?
There’s a condition called “Secondary cataract” or “after-cataract” which occurs when your lens membrane wasn’t removed properly during the surgery, get cloudy and impairs your vision. Treating secondary cataract is very simple. It involves YAG laser capsulotomy- a technique where a laser beam makes a small opening inside the clouded capsule which lets light to pass through it. It is a painless outpatient procedure which can be done in less than five minutes. Most patients gain improved vision immediately.
f you’re exploring vision correction options beyond cataract removal, read about LASIK surgery, a popular procedure to correct nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism. For full details, see our article: LASIK Surgery.