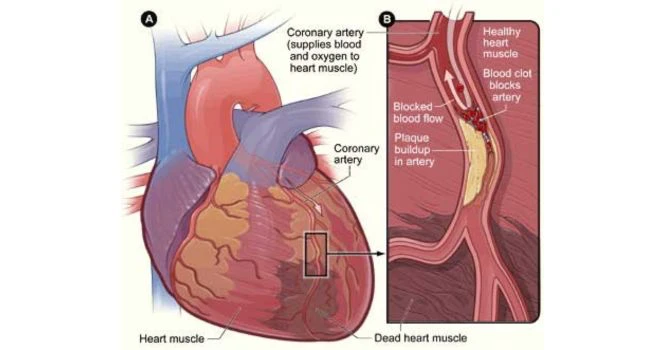
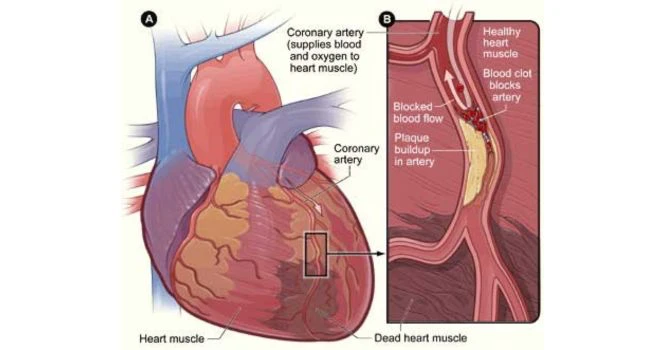
When the blood flow in any one of the coronary arteries is blocked, it’s called Myocardial Infarction and we commonly call it, Heart Attack.
It can be fatal and follows a different course in different patients according to the site of blockade, pre-existing conditions and family history of heart disease.
Depending on the percentage of lumen occluded, it may be a partial block or a complete block.
It’s usually in terms of percentage of blockade.
Note that Conduction blocks are different from the physical blockade as seen in Heart attack or Myocardial infarction
Warning Signs of Heart Attack:
Chest discomfort: Most heart attacks involve discomfort in the center of the chest that lasts more than a few minutes, or that goes away and comes back. It can feel like uncomfortable pressure, squeezing, fullness or pain. Most of the time, the patient explains the pain with a clenched fist or like an elephant sitting on his or her chest, with many of them sweating profusely.
Discomfort in other areas of the upper body. Symptoms can include pain or discomfort in one or both arms, the back, neck, jaw or stomach.
Shortness of breath with or without chest discomfort.
Other signs may include breaking out in a cold sweat, nausea or lightheadedness or may present without any signs and symptoms.
When to consult the doctor?
There is always a tendency to think of signs and symptoms, as minor conditions, associating with your previous meal or missed meal or gastritis, Since this can take your life away, it’s always important to keep handy the list of local emergency numbers to call and go to a nearest tertiary care hospital.
What can you do to avoid a heart attack?
• Don’t smoke, and avoid second-hand smoke.
• Check your blood pressure regularly and take medicines for it,
if prescribed.
• Eat foods that are low in saturated fat, trans fat, sodium or salt and added sugars.
• Be physically active.
• Maintain BMI within normal range.
• Get checked for diabetes and keep blood sugar in normal
range,if you have diabetes.
• Get regular medical check-ups.
• Take medicine as prescribed for your health conditions.
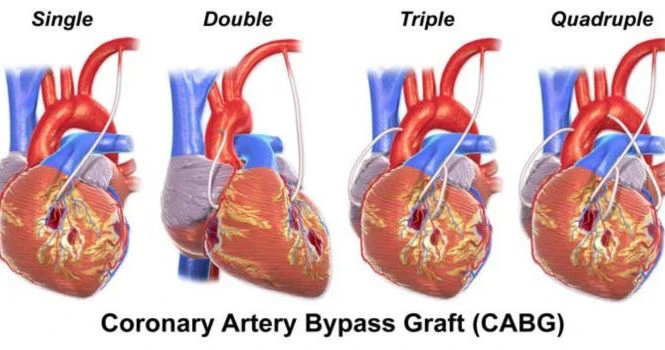
Medical Managements with drugs is usually recommended for blockages less than 50% of the lumen and if the degree is more, then doctors would recommend going in for angioplasty or bypass surgery considering many other factors.
In some cases, the heart reacts to plaque blockade by creating collaterals, but usually insufficient to bridge the gap, thereby causing ischemic injury to the heart.
The Treatment of choice is Per-Cutaneous Coronary Angioplasty, which restores the blood flow.
The stent is placed at the site blockade during Coronary angioplasty.