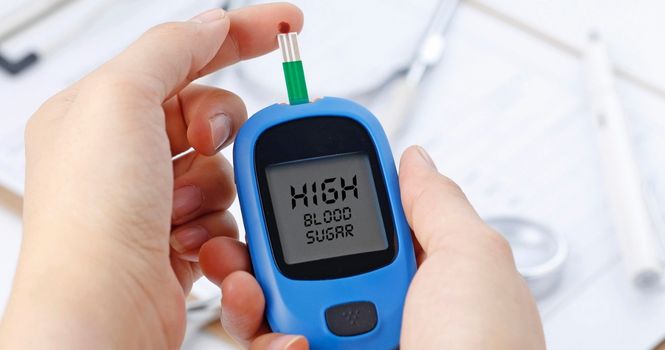
If you find your Blood Sugar is High, then Consult Your Doctor and discuss your medical history and medications you are on.
Having High Blood Sugar is risky and will lead to many complications. However, you might be wondering, just how high is too high?
Let’s get few basics right,
Normal Blood Sugar Levels
For most adults without diabetes, normal blood sugar levels are defined as follows:
- Fasting (after not eating for at least 8 hours): 70 to 99 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL)
- Two hours after eating (postprandial): Less than 140 mg/dL
- Random (at any time): Less than 125 mg/dL
Blood Sugar Levels for Diabetics who are on Medication
Blood sugar targets can vary depending on the individual and their specific health conditions. However, the American Diabetes Association suggests the following targets for most adults with diabetes:
- Before meals: 80 to 130 mg/dL
- One to two hours after the start of a meal: Less than 180 mg/dL
Keep in mind, the target can be different for pregnant women, elderly people, or those with other comorbidities. It’s always best to consult with your doctor or healthcare provider for personalized targets.
Now at,
What Level Of Blood Sugar Is Considered Dangerous?
A blood sugar level below 70 mg/dL is generally considered hypoglycemia, which can be dangerous if not treated promptly.
A blood sugar level above 180 mg/dL may indicate hyperglycemia, a condition associated with poorly controlled diabetes.
If blood sugar levels stay too high for too long (above 240 mg/dL), it can lead to Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA), a Medical Emergency.
The highest blood sugar level that can be read on most glucose meters is typically around 600 mg/dL.
If your glucose meter reads “HI,” this means that your blood sugar level is above the meter’s measurable range, which is a serious, potentially life-threatening situation that requires immediate medical attention.
If you are avoiding visiting your doctor, then it’s important to know that having high blood sugars for long time is dangerous and If left untreated, it can lead to severe complications, including diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state (HHS), which are life-threatening emergencies.
Blood glucose levels are typically monitored using a blood glucose meter, a small device that measures the concentration of glucose in your blood.
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) can also be used, particularly for people with diabetes, as these devices provide real-time glucose readings, allowing for more detailed tracking and better blood sugar control. However, a laboratory test is often the most accurate way to measure blood sugar.
Remember to keep your blood sugar levels within the Normal Range as Low blood sugar is also a Medical Emergency.
Conclusion
Blood sugar plays a vital role in our body’s functioning, and maintaining it within a healthy range is crucial. Both high and low blood sugar levels can be dangerous and life-threatening.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia, knowing your individualized target ranges, and taking appropriate actions can make a significant difference in preventing complications.
Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice on managing your blood sugar levels.