Synonyms of Dengue
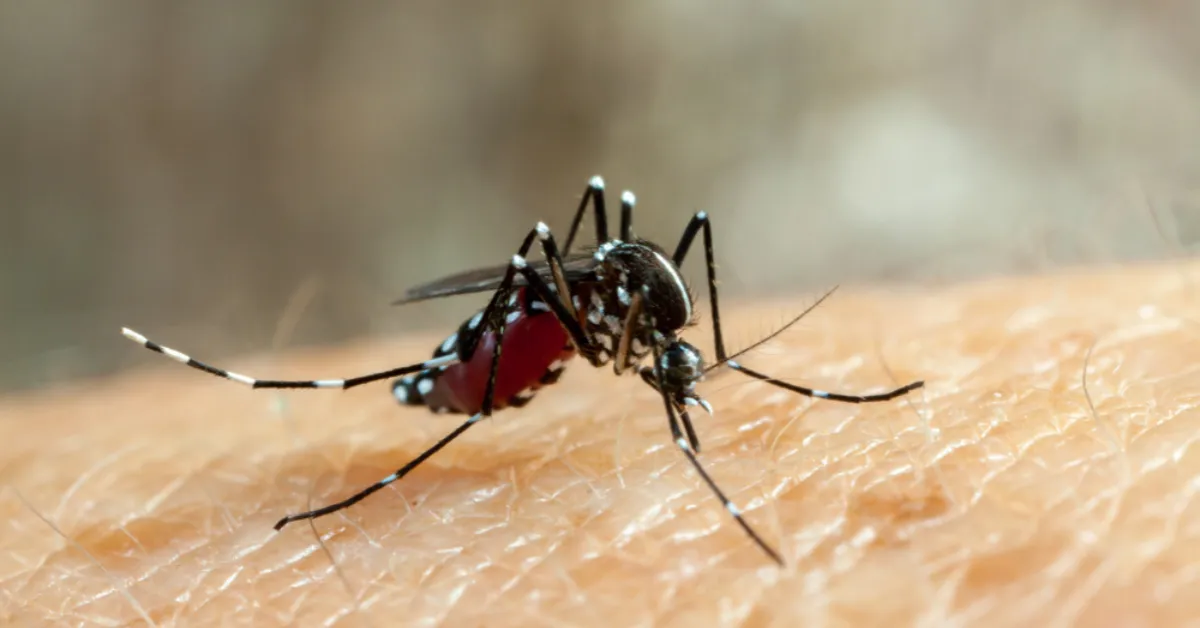
Dengue fever, Breakbone fever, Dengue Hemorrhagic fever, Dengue shock syndrome, Dandy fever.Dengue virus belongs to the arboviruses group of viruses, which infect humans through Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. All ages and both sexes are susceptible to the dengue virus
What is Dengue Fever?
When an infected dengue mosquito bites, the virus is transmitted to the person and the time required for the appearance of the first symptom, which is also called incubation period, is 3 to 10 days (commonly 5 to 6 days). This first symptom is Fever and is called Dengue fever.
Agent which causes Dengue Fever: Dengue Virus
Vector which causes Dengue Fever: Female Aedes Aegypti and Aedes Albopictus Vector is a carrier of disease
Dengue Virus Serotypes
There are 4 virus serotypes which are
- DENV-1
- DENV-2
- DENV-3
- DENV-4
All 4 serotypes are antigenically similar, but different enough to offer cross protection for a few months, to any one of them.
The probability of having a serious form of dengue infection increases with second time infection with Dengue serotype 2 or DENV-2 , or with multiple infections with different serotypes.
Vectors of Dengue Virus (Carrier of the disease)
Female Aedes aegypti is a nervous feeder, it bites more than one host to complete a blood meal and is a discordant species ( it needs more than one meal to complete a gonotropic cycle) and this leads to multiple cases in the city and is the most common vector associated with Dengue Fever.
The other Vector is Aedes Albopictus is concordant species, which means it can complete it’s blood meal with only one bite from a single person and doesn’t need a second blood meal to complete the gonotropic cycle.
Aedes mosquitoes are easily distinguished by white stripes on a black body.
Disease caused by Aedes Aegypti
Because of their striped legs, they are called Tiger Mosquitoes. They are more abundant during rainy seasons.
It breeds in artificial accumulation of water around human dwellings, like in pots of water, stagnant water on roads, or containers on the terrace where rain water has accumulated.
The females are fearless nervous biters and they bite during the day. Their area of flight is restricted to within 100 meters or the area of a football ground.
This 100 meters limit of the mosquito is used to keep the international airports and seaports free from all types of mosquitoes for a distance of 400 meters, or else the infection spreads along the flight routes or transportation routes.
Incidence of Dengue Fever Infection
WHO or World Health Organisation reports that around 400 Million infected worldwide, out of which 100 Million infections show signs and symptoms and out of these 20,000 deaths are reported.
Majority of infections remain asymptomatic or self limiting. Self limiting diseases are those which recover without any intervention or treatment.
How is Dengue transferred from Person to Person?
Dengue spreads, when a female aedes mosquito bites an infected person, and later when the same mosquito bites another person, after 8 to 12 days, then the other person gets infected.
This time interval of 8 to 12 days is called Extrinsic Incubation Period.
Once the mosquito is infected, it remains so for the rest of its life.
It also spreads when the infected person travels from one location to another city or country.
Dengue Fever Symptoms
- The onset is sudden with chills and high fever
- Intense headache
- Muscle and joint pain
- Pain behind the eyes (Retro-orbital pain)
- Photophobia
- Extreme weakness
- Anorexia
- Constipation
- Altered taste sensation
- Colicky Pain (Pain which starts and stops and then comes back)
- Abdominal Tenderness
- Dragging pain in inguinal region
- Sore throat
- General Depression
Classical Dengue fever
The onset is sudden with fever going up to 39℃ to 40℃ (102.2 ℉ to 104℉)
The conversion formula from Celsius to Farenheit is ℃ = 5/9 (F-32)
Dengue Fever has 2 phases
In the First phase, the temperature rises abruptly and then in many cases, comes down within a few hours to 2 days.
In the second phase which lasts for 1 to 2 days, Skin eruptions or rashes are seen in the face, neck and chest which are fleeting pinpoint eruptions . It starts on the chest and trunk and may spread to extremities and rarely to the face. The rask may be itchy and skin may become sensitive ( Hyperaesthesia ).
Fever lasts for about 5 days and rarely 7 days.
Dengue Hemorrhagic fever
It’s a severe form of Dengue fever and can be divided into
- Febrile Phase
- Critical Phase
- Recovery Phase
Febrile Phase
This phase resembles classical dengue fever initially but the rash is less commonly seen. It may appear early or late in the course of illness.
The 2 things that differentiates it from Classical Dengue fever are
- Plasma Leakage
- Abnormal Haemostasis
Tourniquet test is Positive.
The Tourniquet test is performed using the Blood pressure cuff . It is inflated to the midpoint between the systolic Blood Pressure and Diastolic Blood Pressure for 5 minutes. ( If the patient blood pressure is 120/80 mm of Hg, then the cuff is inflated to 100 mm of Hg)
The test is considered Positive when 10 or more petechiae per 1 square inch
(2.5 cm x 2.5 cm) are seen. In Dengue Hemorrhagic fever the test usually gives a definite positive with 20 petechiae or more.
Petechiae are small red spots of bleeding seen under the skin.
When you place your hand on the back or on the forearm, then impressions of your fingers are seen as white. That’s why it is called , “White islands in the sea of red”.
A rapidly decreasing platelet count with rising hematocrit, compared to the patient’s baseline, means the condition is heading towards plasma leakage or critical phase. ( Plasma is liquid portion of the blood)
One should be very cautious , when the temperature declines as this is where the patient can go in the critical phase.
Critical Phase
When the temperature drops down to 37.5℃ – 38℃, and remains low , usually on days 3 to 7 of illness. The increase of capillary permeability and increase in hematocrit levels are observed. This period of clinically relevant plasma leakage lasts for 24 to 48 hours.
WBC decreasing progressively and rapid decrease of platelets, usually precedes plasma leakage. (Plasma is liquid portion of the blood)
At this point, patients without an increase in capillary permeability improves and those with increased capillary permeability worsen.
Recovery Phase
If the patient survives the 24 to 48 hours of critical phase, then there is gradual reabsorption of the leaked fluid.
Dengue Shock syndrome
Shock occurs when a critical volume of plasma is lost through leakage. It is preceded by warning signs such as,
- Abdominal pain and tenderness
- Persistent vomiting
- Fluid accumulation
- Mucosal bleeding
- Lethargy
- Restlessness
- Liver enlargement > 2 cm
- Scanty Urine
The following Dengue Diagnostic Lab Tests would help to confirm the diagnosis of dengue
Dengue Blood Tests
Laboratory investigations are important for rapid and accurate diagnosis . It can be done at any time of the day or night and fasting is not required. Blood is taken from a vein in a red or yellow tube . The following methods are employed.
Virus detection Methods
Virus isolation is not a practical measure as it takes weeks for the report to arrive.
Viral Nucleic acid detection
Dengue viral genome, which consists of single stranded, enveloped Positive sense RNA, can be detected by RT-PCR test, the results of which can be available in 1 to 2 days.
Viral antigen detection
NS1 Rapid tests are inexpensive and give results in minutes. NS1 Ag ELISA gives a report in one day.
Immunological response and serological tests
Serum after day 5, IgM by Rapid tests gives a report in minutes, while Elisa takes 1 to 2 days.
Analysis of Hematological parameters
Platelet count and hematocrit are important values and would be tracked by your doctor.
How to read Dengue Test Report
Serological detection is a common method for the diagnosis of infection with dengue viruses. IgM anti-dengue antibodies start to appear 3 days after initial exposure and remain in the circulation for about 30-60 days.
IgG anti-dengue antibodies rise at around 7 days, peak at 2-3 weeks, and persist for life.
1. If Dengue NS1 Test is positive
It means the Dengue Virus Antigen is present and confirms the Dengue virus infection. It doesn’t tell about the serotype of the virus. It’s a card test and results are available within minutes.
2. Dengue igM Positive
It means that Dengue igM antibodies are present in your blood and it is the first immunoglobulin or antibody to appear . It denotes RECENT infection. Dengue IgM antibodies start to appear 3 days after initial exposure and remain in the circulation for about 30-60 days.
3. Dengue test igG positive
It means Dengue igG antibodies to dengue virus are present and they start appearing around 7 days, peak at 2 to 3 weeks and once infected, they tend to remain in the body for life. The test may be positive, if you were previously infected with dengue.
If Dengue Test isreported as Non Reactive, then it means that there are no dengue virus antibodies present in your blood.
The following are the High Risk patients, in whom the course of the disease might be more severe
High risk Patients
- Infants
- Elderly
- Obesity
- Pregnant woman
- Menstruating women or with abnormal bleeding
- Thalassemia
- Diabetes
- Hypertension
- Asthma
- Heart disease
- Chronic renal failure
- Liver cirrhosis
- Patients on steroids
- Patients taking NSAID like aspirin
Dengue Fever Treatment
Treatment depends on the severity of the disease.
A complete blood count is done which forms the baseline for reference to check for improvement or if it is getting worse.
The Normal values are given here,
Normal Platelet count : 1.5 lakh to 4.5 lakhs/cmm2
Normal Hematocrit values are
- ● For men, 38.3 to 48.6 percent
- ● For women, 35.5 to 44.9 percent
WBC count : 4000 to 11,000 cells/cumm
Patients should take adequate oral rehydration solutions or ORS containing electrolytes and sugar to replenish the losses from fever and vomiting. Paracetamol 500 mg every 6th hourly can be taken, which is available over the counter.
DON’T take Aspirin, ibuprofen or NSAID or any pain killers as it may aggravate gastritis or bleeding.
The caregivers must closely monitor the patient and the patient brought to the hospital, These are called as,
Warning signs of Dengue
- No improvement in the condition
- Condition of the patient is worsening when the fever is decreasing.
- Severe abdominal pain
- Persistent vomiting
- Cold hands and feet
- Extreme tiredness
- Restlessness
- Stools which are black in colour
Black stool indicates that bleeding is from the upper GIT, esophagus, stomach or small intestine. Red coloured stools indicate bleeding from the colon, rectum and anus.
What to EAT during Dengue Fever?
While increasing the fluid intake along with electrolytes, you can eat green leafy vegetables, broccoli and sprouts, which are good sources of vitamin K, which is essential for Blood clotting and increasing the platelets.
You can eat oranges, pineapple, kiwi fruit , coconut water helps in rehydration, Legumes, which are a source of iron, along with rice, potato and milk.
Avoid carbonated beverages,Tea, coffee and energy drinks which make you dehydrated.
AVOID, Fatty and oily food , while spicy food promotes acid build up in the stomach and increases the risk of GI bleeding .
Avoid Non-Veg food and keep your diet Bland till you recover.
PREVENTION FROM DENGUE
While the patient is recovering, Other family members in the household should take preventive measures to protect themselves from mosquitoes.
- Isolation of the patient under bed-nets during the first few days, to protect him from mosquitoes, which may bite him and infect others at home.
- Use mosquito repellant and wear full sleeve shirts and trousers, and apply mosquito repellent creams to the exposed body parts.
- Make sure the doors and windows are closed before it gets dark. Mosquito mesh doors and windows to be covered in mosquito mesh is preferred.
- While you kill all the mosquitoes, make sure you sleep under the mosquito bed-net.
- Make sure you check the surroundings for water accumulating in any containers, and drain the stagnant water.
- Just keeping yourself safe is not enough, make sure you spread the word in the community and educate and encourage others to take steps to remove stagnant water, whenever they see them, as mosquitoes are born there.
DENGUE VACCINE
CYD-TDV DENGVAXIA is a prophylactic, tetravalent, live attenuated viral vaccine developed by Sanofi Pasteur in December 2015. It’s given in Dengue endemic regions.
Live attenuated vaccine is when the dengue virus is weakened in such a way that they can elicit an immune response, but are not able to cause the disease in healthy persons. It’s not available in India now and might be available in 2 to 4 years.
Question and Answers on Dengue Fever
1. Can dengue happen twice?
Yes. and that’s the danger . The person having second time dengue are reported to have more complications and severe form of the disease.
2. Why do dengue mosquitoes bite in the daytime? Can a dengue mosquito bite at night?
They are primarily day time biters and mostly active during mornings and before dawn. They can also bite at night time.
3. Which dengue serotype is most dangerous?
There are 4 serotypes , DENV1 DENV3 DENV3 DENV4, and out of these DENV2 is
reported to be more virulent.
4. How far does a dengue mosquito fly?
It can fly around 100 m , which is the size of the football field . But if an infected person travels, then it can be transmitted to other areas and cities. That’s why the spread of transmission is along the transportation routes. That’s why you hear doctors advising curbing travel then there is a burst in cases.
5. Why is dengue known as breakbone fever?
It’s because of the joint pain and severe muscle pain associated with it.
6. Are dengue rashes itchy?
Yes . It may be itchy and the skin would become more sensitive, also called hyperaesthesia.
7. Dengue without fever symptoms?
Yes. around 80% of the patients can have dengue without any symptoms. It is self limiting and resolves without any intervention.
8. What is Nipah Virus ?
Nipah virus is a zoonotic virus transmitted from animals to humans, causing severe respiratory illness and encephalitis. It has a high fatality rate and can spread through direct contact with infected animals, their secretions, or contaminated food. Human-to-human transmission is also possible.